October 21, 2025 | Policy Alerts
Policy Alert: Legislative Action Plan for Gaza Peace Implementation
October 21, 2025 Policy Alerts
Policy Alert: Legislative Action Plan for Gaza Peace Implementation
Bottom Line Up Front
On October 13, 2025, President Donald J. Trump, joined by leaders from Egypt, Qatar, Turkey, and other countries, backed a historic peace plan at Sharm El-Sheikh to end the two-year Gaza conflict. This plan achieved the immediate release of the hostages and established a framework for a comprehensive ceasefire, to include Gaza’s eventual phased demilitarization under international oversight. Drawing on the spirit of the 2020 Abraham Accords, the plan aims to dismantle Hamas’s terror infrastructure, rebuild Gaza as a deradicalized zone, and lay a foundation for lasting peace.
As Vice President JD Vance visits the region today to keep the deal on track, Congress has a decisive role to play in ensuring the plan’s successful implementation through legislation, oversight, and enforcement. History shows that Middle East peace frameworks often fail not in their design, but in their execution, and the window for Congressional action is narrow. Below we break down the framework’s provisions and timeline, lay out why its success matters, and identify what Congress can do to increase its chances of working.
Estimated reading time: 9 minutes
FDD Action Expert Analysis

“President Trump’s peace plan marks a monumental breakthrough that opens the door to achieving lasting stability in a region long plagued by conflict. But whether this ceasefire translates into enduring peace will depend on how committed Congress and the Trump administration remain to its rigorous enforcement. This agreement must be vigorously enforced at every stage, with zero tolerance for any violation, no matter how minor. Congress has a critical and ongoing responsibility to shape its implementation, providing necessary oversight and ensuring that U.S. policy and assistance align with the goals of peace and security. By permanently and verifiably dismantling the terrorist infrastructure in Gaza, conditioning aid on compliance, and supporting diplomatic and enforcement measures, lawmakers can help safeguard the peace and promote a stable future.”
What the Framework Contains
- Immediate ceasefire: An enforceable cessation of hostilities across all fronts.
- Hostage release: All remaining Israeli hostages freed, and the remains of 28 returned.
- Prisoner exchange: Approximately 2,000 Palestinian terrorists and facilitators released from Israeli custody.
- Israeli withdrawal: Forces repositioned to agreed perimeter lines in Gaza.
- Humanitarian access: Aid convoys proceeding under international verification.
- Phased demilitarization: Supervised dismantlement of the terrorist infrastructure in Gaza to include the disarmament of Hamas and allied groups.
- Stabilization framework: Deployment of a multinational force to ensure security.
- Reconstruction mechanism: Launch of an internationally funded board to restore Gaza’s infrastructure and services.
Implementation Timeline and Phasing
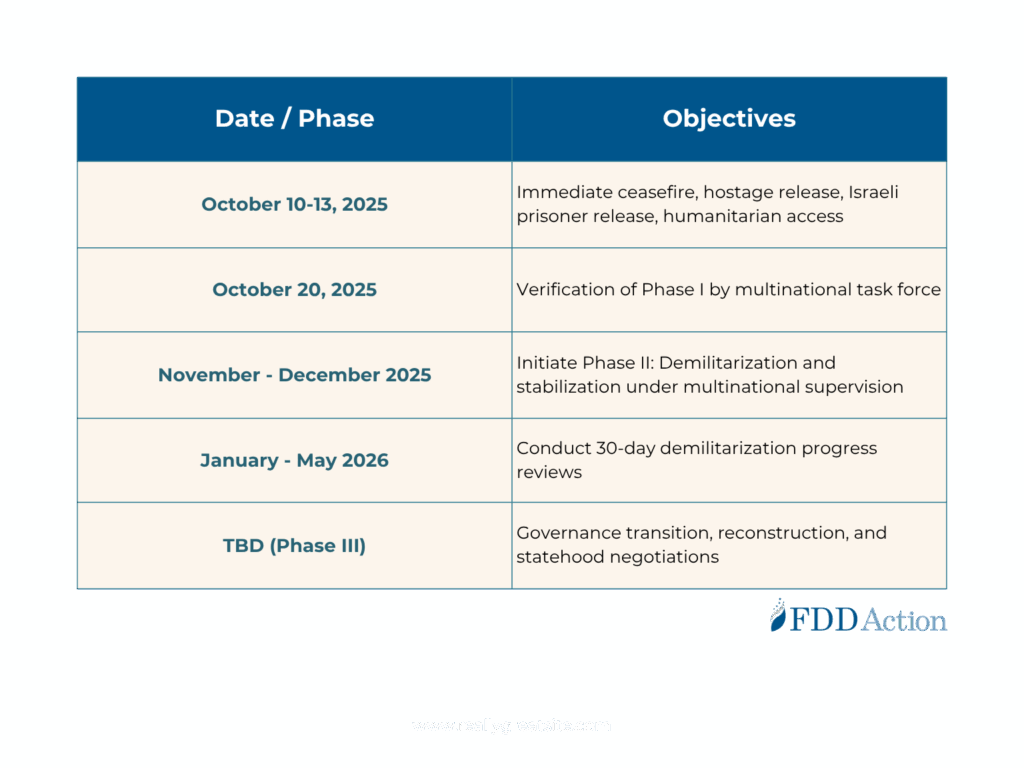
Phase I: Ceasefire and Hostage Release
- Achieve immediate and verifiable ceasefire.
- Secure release of living hostages and remains of deceased.
- Free approximately 2,000 Palestinian prisoners.
- Withdraw Israeli forces to agreed boundaries.
- Allow humanitarian aid to resume.
Status:
- Ceasefire: Incomplete
- Hostage and remains transfer: Incomplete
- Prisoner release: Complete
- Israeli withdrawal: Complete
- Humanitarian access: Complete
Phase II: Demilitarization and Security Stabilization
- Begin phased disarmament of Hamas and militant factions.
- Deploy international stabilization force and vetted Palestinian elements.
- Prevent renewed attacks or violations.
- Ensure no Israeli annexation or forced displacement.
Status:
- Demilitarization: Not Started
- Stabilization deployment: Not Started
- Transition security verification: Not Started
Phase III: Governance Transition and Reconstruction
- Form a technocratic, independent Palestinian authority under international supervision.
- Rebuild Gaza’s public infrastructure and essential services.
- Launch an internationally managed reconstruction board.
- Begin long-term negotiations on future Palestinian statehood following full demilitarization.
Status:
- All steps: Not Started
Why the Deal Matters for U.S. National Security
The Trump administration’s framework is more than a ceasefire, it is a test of America’s ability to not only end wars, but to shape what comes after them. The United States now faces a choice: either lead the enforcement and long-term architecture of this agreement, or leave a vacuum that Iran, Russia, or China will eagerly fill once the dust settles. If Washington backs this process with sustained diplomatic leverage, strong congressional oversight, and robust enforcement tools, it can transform a fragile truce into a durable regional realignment that advances U.S. security, economic, and counterterrorism interests for decades to come. Here’s just a few reasons why that matters:
Promotes U.S. strategic credibility: Successful implementation of the deal will strengthen American leverage in Middle East diplomacy by solidifying Washington’s position as the indispensable partner behind conflict resolution and peacebuilding. If successful in the long-term, it will underscore the United States’ ability to translate military and economic influence into sustained diplomatic outcomes that adversaries like China or Russia cannot match.
Reduces Iran’s influence: If Washington sees this through, such a peace will weaken Tehran’s network of proxies, undercutting the political legitimacy and funding streams that sustain groups like Hezbollah, the Houthis, and Hamas. Coordinated pressure on these entities isolates Iran’s regional agenda and limits its capacity to reconstitute and project asymmetric power across multiple fronts.
Advances counterterrorism goals: An agreement that holds will also see Gaza’s terrorist infrastructure dismantled, denying extremist networks territorial and financial sanctuaries with which to plan attacks against Israel, the United States, and our allies and partners. In parallel, U.S.-led partnerships will emphasize governance and reconstruction mechanisms designed to prevent terrorist resurgence in Gaza and neighboring areas.
Expands long-term U.S. economic and energy interests: Peace will open space for regional reconstruction initiatives and trade corridors linked to new energy integration efforts. By expanding the Abraham Accords to additional states, the U.S. positions itself to anchor a connected Middle East economy aligned with Western standards on investment, security, and technology exchange.
What Congress Should Do Next
Congress must act decisively to ensure this framework succeeds where past agreements have failed. Without sustained legislative oversight, enforceable accountability measures, and strategic use of U.S. economic and diplomatic leverage, the administration’s framework risks becoming another well-intentioned plan undermined by weak implementation and unchecked violations.
Lawmakers should move immediately to condition all assistance on verified compliance with the agreement’s core provisions, particularly the dismantlement of Hamas’s terrorist infrastructure and the end of incitement. By strengthening sanctions enforcement, expanding trade incentives tied to the Abraham Accords, and combating international lawfare against U.S. allies, Congress can transform this ceasefire into a durable regional realignment that serves American national security interests for generations to come.
Legislative Oversight and Enforcement Tools for Assistance
- Revise Sections 620K and 620L of the Foreign Assistance Act to freeze Economic Support Funds allocated to Gaza and the West Bank until the U.S. verifies that Hamas’s terrorist infrastructure is fully dismantled.
- Strengthen certification requirements under the Palestinian Anti-Terrorism Act of 2006 to ensure no ministry, agency, or instrumentality of the Palestinian Authority (PA) employs Hamas members, agents, or affiliates, and guarantee strict vetting so that no U.S. assistance to nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) operating in the territories benefits Hamas or any terrorist group, either directly or indirectly.
- Strengthen and expand Taylor Force Act provisions, conditioning all U.S. funding to the PA on a verified end to its “pay-to-slay” program that provides stipends to terrorists and their families, by preventing any direct or indirect benefit from American assistance until this practice ceases fully.
- Codify the Sec. 301 ban on U.S. contributions to the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees (UNRWA) and ensure that any U.S. assistance to international organizations or NGOs operating in Gaza or the West Bank is predicated on a strict and publicly attested “no contact” policy with Hamas or any other U.S.-designated terrorist groups or affiliates. This policy must prohibit direct or indirect interaction, require publicly available independent audits verifying compliance, and ensure that aid distribution mechanisms operate outside of Hamas’s influence or control.
- Impose targeted sanctions on individuals and entities violating the framework agreement using authorities under the Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO) statute, Executive Order 13224, and statutory sanctions from legislation, including the Fiscal Year 2024 supplemental appropriations bill that mandates the application of sanctions on foreign government agencies providing material support to Hamas.
- Pass legislation like H.R. 4397 to formally designate the Muslim Brotherhood and its affiliates as FTOs, cutting off Hamas’s access to international financial networks and ideological support structures that enable reconstitution. This critical step closes pathways for Hamas to rebuild through Brotherhood-linked entities and ensures comprehensive isolation from the global financial system.
Ensure Allies and Partners Expand Sanctions on Hamas
- Call on key partners in the Abraham Accords and those in attendance at the Sharm El-Sheikh conference, particularly Qatar, Turkey, Kuwait, and Jordan, to align their domestic sanctions regimes with the U.S. Treasury’s OFAC Specially Designated Nationals (SDN) list on Hamas and other organizations operating in the West Bank and Gaza. This alignment would involve adopting equivalent asset freezes, travel bans, and financial transaction prohibitions on US SDN-listed entities, like the multilateral coordination seen in dozens of countries that synchronize with OFAC on Russia-related sanctions. Congress and the Trump Administration should formally request this coordination and condition bilateral assistance and trade benefits on demonstrable progress toward sanctions alignment.
Advance Deradicalization and Anti-Incitement Measures
- Authorize a Deradicalization Accountability Task Force mandated to report annually to Congress on progress in deradicalization programs implemented in the West Bank and Gaza. Explicitly require the Secretary of State to certify that PA educational materials and public messaging comply with anti-incitement standards before funds are released, similar to bipartisan legislation like the Peace and Tolerance in Palestinian Education Act that passed the House of Representatives in the 118th Congress.
Combat International Lawfare
- Codify sanctions on International Criminal Court (ICC) officials who pursue politically motivated cases against the U.S. or Israel. Congress should mandate visa bans, asset freezes, and diplomatic restrictions consistent with existing punitive measures for international legal overreach. H.R. 23, the Illegitimate Court Counteraction Act, passed the House earlier this year with bipartisan support and should be taken up in the Senate.
- Amend the American Servicemember’s Protection Act to broaden prohibitions beyond barring U.S. government cooperation with the ICC. Specifically, legislation should bar all American individuals, companies, and entities from furnishing information, data, or assistance, directly or indirectly, to the ICC or its officials in cases involving U.S. personnel or allied nations like Israel. This provision would close loopholes that permit private cooperation with ICC investigations that undermine U.S. sovereignty and allies, complement existing executive orders targeting ICC activities, and codify these prohibitions into law.
Create Economic Incentives Aligned with the Abraham Accords
- Expand trade and investment benefits to offer preferential trade agreements and tariff reductions specifically conditioned on countries advancing normalization with Israel under the framework of the Abraham Accords. This leverages the trade and economic integration momentum established by accords signatories like the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, and Morocco, incentivizing new partners to join or deepen engagement.
- Develop collaborative innovation hubs, R&D initiatives, and workforce exchange programs connecting the U.S. and Israel with existing and prospective Abraham Accords partners. Highlighting shared economic interests fosters people-to-people ties and generates greater support for normalization.
- Establish grant programs and funding mechanisms to finance cross-border projects in transportation, energy, and water management, linking Israel with fellow Abraham Accords countries and beyond. These infrastructure investments embody the accords’ emphasis on comprehensive regional connectivity and shared prosperity as peace dividends.
Additional Resources
- After Gaza’s Deal, A Momentum in the Region for More Peace Stability in Syria, Lebanon? (Seth J. Frantzman | Op-Ed | October 14, 2025)
- Hamas Turns Its Guns on Gaza’s Clans (Ahmad Sharawi | Policy Brief | October 15, 2025)
- FAQ: What To Know About Phase One of the Gaza Ceasefire (Aaron Goren | FAQ | October 10,2025)
- Egypt Says 15 Palestinian Technocrats Approved To Manage Post-War Gaza (Flash Brief | October 14, 2025)
- ‘Blatant Violation of the Deal’: Israel Closes Rafah Border Crossing After Hamas Fails to Release All 28 Deceased Hostages (Flash Brief | October 14, 2025)
- Trump Addresses Knesset as All Living Hostages Return to Israel from Hamas Captivity (Flash Brief | October 13, 2025)
- Trump to Co-Chair Summit on Gaza’s Future During Middle East Visit (Flash Brief | October 12, 2025)
- Why Donald Trump’s Diplomacy Appears to be Working (Seth Frantzman | Op-Ed | October 10, 2025)